
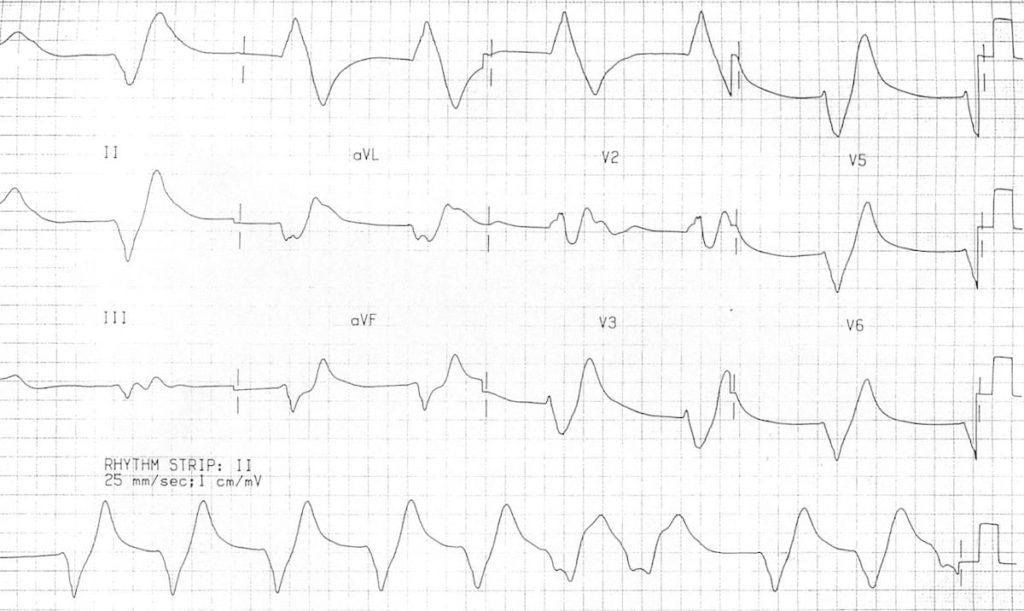
This case report suggests that ECG changes in hyperkalemia may be established not only by the level of hyperkalemia, but also by the development of hyperkalemia. TYPICAL ECG FINDINGS The earliest ECG signs of. At this admission, the ECG showed sine-wave ventricular tachycardia (VT) ( Picture 2). Pseudohyperkalemia results when potassium is released from platelets in the setting of thrombocytosis. However, he returned five days later due to the deterioration of his general condition and hyperkalemia (serum potassium, 8.6 mEq/L). Tall tented T-waves or peaked T waves are shown in the precordial leads or chest leads. The patient selected best supportive care, rather than chemotherapy, for his cancer and was discharged six days after admission. This video shows an ECG of a patient with hyperkalemia. His hyperkalemia improved following the discontinuation of these medications and administration of sodium polystyrene sulfonate. Hyperkalemia was caused by tumor lysis syndrome from gastric cancer and medications, including enalapril, carvedilol, and spironolactone. Burns, E.A 77-year-old man with chronic kidney disease was admitted to our hospital due to acute kidney injury and hyperkalemia (serum potassium, 8.5 mEq/L) with a normal ECG finding ( Picture 1).In Current diagnosis & treatment emergency medicine. Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Emergencies. **Caution in patients with DKA because total body potassium may actually be low and aggressive management of hyperkalemia can result in hypokalemia** Kayexalate (Sodium polystyrene sulfonate) can be used to promote potassium elimination from the body, however this has no role in the acute management of hyperkalemia with EKG changes.Albuterol and Sodium bicarbonate can also be used to promote the movement of potassium into cells depending on potassium levels.Insulin to promote the movement of potassium into cells.Usually reserved for K>7.0 or EKG changes. Calcium (either IV calcium gluconate or calcium chloride), which stabilizes cellular membranes by antagonizing the effect of potassium on membrane potential.We report data on seven patients with renal failure. Given the broad differential for these ECG changes, hyperkalemia has been dubbed the Great ECG Imitator. Severe hyperkalemia with minimal or nonspecific electrocardiographic (ECG) changes is unusual. Pseudohyperkalemia refers to artificially elevated potassium due to: (a) Hemolysis. These ECG findings are not specific to hyperkalemia alone. Hyperkalemia is variably defined as potassium >5.5 mM or >5.0 mM, depending on the source. Typical management of hyperkalemia (for K>6.0 or EKG changes) includes**: There should always be a high suspicion for hyperkalemia in any bradycardic patient, especially if there are other EKG findings to suggest hyperkalemia. Post treatment EKG shows much smaller, more typical broad based T waves:įor patients with ESRD on hemodialysis, dialysis is the definitive treatment for hyperkalemia.


The T-wave abnormalities in this EKG are somewhat subtle, but the narrow, “pinched down” bases of the T-waves should warn you of hyperkalemia. The narrow based, peaked T-waves present in this patient’s EKG, most evident in leads V3-V4, indicate probable hyperkalemia in this patient who is at risk for elevated potassium given her ESRD. Normal sinus rhythm at a rate of 77, normal PR interval, normal QRS, normal axis, LVH (significantly increased voltages), narrow based, peaked T-waves, T-wave inversions in leads III and aVF. hyponatremia and hyperkalemia, as well as the evaluation of patients with hyponatremia or hyperkalemia, are discussed elsewhere: Hyponatremia and hyperkalemia are the two major Mineralocorticoid replacement is required in most patients with primary adrenal insufficiency. What finding on this EKG warrants further management?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
